Table of Contents
Tech Innovations for Urban Living That Will Shape Future
In the relentless pulse of urban life, a profound transformation is underway — the rise of smart cities. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, the intersection of technology and urban living gives birth to a dynamic landscape where innovation shapes the very fabric of our cities. Welcome to a journey through “Smart Cities, Smart Startups: Tech Innovations for Urban Living.”
This blog invites you to explore the cutting edge of urban evolution, where cities become intelligent ecosystems, leveraging technology to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and the quality of life for their inhabitants. From the intricate integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) that weaves a digital nervous system within city limits to the sustainable mobility solutions redefining how we traverse urban spaces, each topic unravels a chapter in the story of smart cities.
Embark on a voyage through artificial intelligence, data-driven governance, and the revolutionary concept of augmented reality in urban planning. Witness the metamorphosis of homes into smart living spaces and delve into the realms of digital health, where technology converges with well-being. Join us as we unravel the potential of blockchain applications safeguarding city operations and delve into the critical domain of cybersecurity fortifying the digital urban landscape.
The smart city landscape is a canvas painted with diverse hues of innovation, and this blog is your guide to navigating this frontier. As we delve into each technological facet, envision the future of cities not just as centers of population but as hubs of ingenuity, sustainability, and interconnected brilliance. The urban frontier beckons, and the possibilities are limitless. Join us on this exploration of smart cities and the tech innovations propelling us towards a future where urban living is not just smart but truly transformative.
Here are some of the dimensions that you can imagine with the real world happenings:-
1. IoT Integration: Building the Nervous System of Smart Cities
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) serves as the bedrock for the transformation of conventional urban landscapes into intelligent and responsive smart cities. Unlike the static nature of traditional cities, smart cities leverage IoT technologies to create a dynamic and interconnected environment. This integration involves embedding sensors and smart devices throughout the urban infrastructure, facilitating the seamless exchange of data in real-time.
Consider the realm of transportation within smart cities. Traffic management is revolutionized with IoT-enabled traffic lights and sensors that gather real-time information about traffic patterns. This data is then analyzed to optimize signal timings, thereby reducing congestion and enhancing the overall efficiency of the transportation network. In Singapore, for instance, the Smart Nation initiative employs IoT to manage traffic congestion, leading to smoother traffic flow and reduced travel times.
Furthermore, waste management systems in smart cities utilize IoT sensors placed in garbage bins. These sensors monitor the fill levels of bins, providing valuable insights that enable optimized waste collection routes. This not only improves the efficiency of waste management but also contributes to environmental sustainability by minimizing unnecessary vehicle emissions.
The integration of IoT extends into the public services domain as well. Smart street lighting, equipped with motion sensors and intelligent controls, adjusts lighting levels based on real-time conditions. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to public safety by ensuring well-lit streets when needed. Emergency services benefit from IoT-enabled surveillance cameras that transmit real-time data to law enforcement, aiding in crime detection and response.
In essence, the integration of IoT in smart cities establishes a sophisticated network, akin to a nervous system, that constantly gathers, processes, and acts upon data. This interconnectedness not only optimizes urban operations but also fosters a city that is adaptable, efficient, and attuned to the needs of its inhabitants. As cities continue to evolve, leveraging IoT technologies becomes instrumental in creating urban environments that are not only smart but also sustainable and resilient. This approach signifies a transformative shift towards cities that prioritize innovation for the betterment of the community and the environment.
2. Sustainable Urban Mobility: Redefining Transportation with Tech

In the landscape of smart cities, the paradigm of urban mobility undergoes a profound shift with the incorporation of sustainable and technology-driven solutions. Traditional transportation systems are often plagued by issues of congestion, pollution, and inefficiency. However, the advent of smart technologies is revolutionizing how people move within cities, focusing on creating a more sustainable and seamless urban transportation experience.
One exemplary facet of sustainable urban mobility is the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles. Electric vehicles (EVs) significantly reduce carbon emissions and contribute to cleaner air in densely populated urban areas. Meanwhile, autonomous vehicles hold the promise of optimizing traffic flow, reducing accidents, and improving overall transportation efficiency. Cities like Oslo, Norway, have embraced electric public transportation options, leading to a noticeable reduction in air pollution and a commitment to sustainable urban mobility.
Additionally, the integration of ride-sharing platforms and smart public transportation systems plays a pivotal role in redefining how individuals navigate cities. Apps that enable real-time ride-sharing not only reduce the number of vehicles on the road but also contribute to lowering emissions. Smart public transportation systems leverage data analytics to predict demand, optimize routes, and enhance the overall efficiency of mass transit. For instance, Barcelona’s “Superblocks” initiative combines smart traffic management with pedestrian-friendly zones, promoting sustainable urban mobility and reducing reliance on individual cars.
Furthermore, the advent of micro-mobility solutions, such as electric scooters and bikes, provides last-mile connectivity options, reducing the need for short trips in private vehicles. These solutions are often integrated into smart city ecosystems, allowing users to locate, unlock, and pay for these services seamlessly through mobile apps.
In essence, sustainable urban mobility in smart cities is a multi-faceted approach that combines electric vehicles, autonomous technologies, data-driven public transportation, and innovative micro-mobility solutions. By prioritizing environmentally friendly and technologically advanced transportation options, smart cities aim to mitigate congestion, reduce emissions, and create a more efficient and accessible urban mobility landscape for residents and visitors alike.
3. AI-Powered Infrastructure: Enhancing Efficiency and Resilience

The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into the infrastructure of smart cities marks a transformative leap in enhancing operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and overall resilience. AI serves as the cognitive engine that empowers infrastructure elements to adapt dynamically, responding to changing conditions and demands in real-time.
One notable application of AI in smart city infrastructure is predictive maintenance for critical assets. By employing machine learning algorithms, cities can analyze historical data and predict when infrastructure components, such as bridges or utility systems, are likely to require maintenance. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces costs, and ensures that essential services remain uninterrupted. For example, in Amsterdam, AI algorithms are used to predict maintenance needs for bridges, optimizing repair schedules and minimizing disruptions to transportation.
Moreover, AI contributes significantly to energy management within smart cities. Machine learning algorithms analyze consumption patterns and forecast energy demands, allowing for the optimization of energy distribution and the integration of renewable energy sources. In Copenhagen, AI is utilized to manage the city’s district heating system efficiently, balancing energy usage and minimizing environmental impact.
The deployment of AI extends into public safety as well. Video analytics powered by AI can enhance security surveillance by automatically detecting and responding to unusual activities or incidents. This technology aids law enforcement in preventing and addressing security threats more effectively. For instance, in Singapore, AI-driven video analytics are used to monitor crowded areas, enabling rapid response to potential security issues.
Furthermore, the intelligent utilization of AI in traffic management optimizes transportation flow. AI algorithms process real-time data from various sources, such as traffic cameras and sensors, to dynamically adjust traffic signals, easing congestion and improving overall traffic efficiency. In Los Angeles, AI-based traffic management has demonstrated success in reducing travel times and enhancing the flow of vehicles.
In summary, the infusion of AI into smart city infrastructure empowers cities to operate with unprecedented efficiency and resilience. From predicting maintenance needs to optimizing energy usage and enhancing public safety, AI-driven solutions contribute to a more responsive and adaptable urban environment, ultimately improving the quality of life for city residents.
4. Data-driven Governance: Transforming City Management
The adoption of data-driven governance stands as a cornerstone in the evolution of smart cities, revolutionizing how urban areas are managed, monitored, and optimized. This approach involves leveraging vast amounts of data collected from various sources to inform decision-making processes, enhance service delivery, and improve the overall quality of life for city residents.
One prominent aspect of data-driven governance is the implementation of smart city platforms that aggregate and analyze diverse datasets. These platforms utilize advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to extract actionable insights from the massive streams of data generated by urban systems. For instance, Barcelona’s CityOS platform integrates data from various city departments, allowing officials to monitor everything from traffic patterns to waste management in real-time.
City management benefits significantly from data-driven insights. For instance, predictive analytics can be employed to forecast and mitigate potential challenges such as traffic congestion, enabling authorities to proactively implement measures to improve traffic flow. Additionally, data-driven approaches to waste management can optimize collection routes based on real-time fill levels in bins, reducing operational costs and improving efficiency.
Moreover, data-driven governance enhances public services by personalizing offerings and tailoring resources to the specific needs of the community. For example, healthcare services can be optimized based on health data analytics, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to areas with higher health risks. Similarly, educational services can benefit from targeted interventions based on data-driven assessments of student performance and needs.
Transparency and citizen engagement are also bolstered through data-driven governance. Open data initiatives, where non-sensitive information is made accessible to the public, foster collaboration between the government and citizens. This not only enhances accountability but also allows residents to actively participate in decision-making processes. London’s Datastore is an exemplar, providing citizens with access to a wide array of city data, promoting transparency and encouraging innovation.
In essence, data-driven governance transforms city management into a proactive and dynamic process. By harnessing the power of data analytics, smart cities can respond swiftly to challenges, tailor services to individual needs, and foster a more transparent and engaged relationship between the government and its residents. As cities continue to evolve, the effective use of data becomes integral to creating urban environments that are not only smart but also responsive and citizen-centric.
5. Innovative Energy Solutions: Powering the Urban Future

The integration of innovative energy solutions in smart cities represents a pivotal step towards sustainable urban development, emphasizing the optimization of energy usage, the incorporation of renewable sources, and the reduction of environmental impact. This paradigm shift in energy management plays a crucial role in ensuring the long-term resilience and eco-friendliness of urban areas.
One key facet of this transformation is the adoption of smart grids. Smart grids utilize advanced communication and control technologies to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity distribution. By incorporating sensors and real-time data analysis, smart grids can dynamically respond to changes in demand, reduce wastage, and integrate renewable energy sources seamlessly. For instance, in Tokyo, the Fujisawa Sustainable Smart Town leverages smart grid technology to optimize energy consumption and reduce reliance on traditional power sources.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are integrated into the energy infrastructure of smart cities to diversify the energy mix and reduce dependence on non-renewable resources. Solar panels on buildings, wind turbines in urban areas, and other renewable energy installations contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable energy supply. The city of Masdar in the United Arab Emirates exemplifies this commitment, relying extensively on renewable energy sources for its power needs.
Energy-efficient buildings also play a crucial role in the quest for sustainable urban energy solutions. Smart city initiatives focus on constructing and retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient technologies, such as intelligent lighting, heating, and cooling systems. These systems adapt to occupancy patterns and environmental conditions, optimizing energy usage without compromising comfort. The EDGE Olympic in Amsterdam is a prime example, showcasing a sustainable building design that incorporates energy-saving features.
Moreover, the promotion of electric mobility contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Smart cities encourage the adoption of electric vehicles by establishing charging infrastructure, offering incentives, and integrating electric transportation into public transit systems. For instance, Oslo, Norway, has witnessed a surge in electric vehicle adoption due to a comprehensive strategy that includes incentives, charging infrastructure, and access to bus lanes for electric vehicles.
In summary, innovative energy solutions in smart cities encompass a holistic approach that includes smart grids, renewable energy integration, energy-efficient buildings, and the promotion of electric mobility. By embracing these initiatives, smart cities strive to create a sustainable and resilient urban future, reducing their environmental footprint and ensuring a reliable and efficient energy supply for generations to come.
6. Smart Homes and Connected Living: Revolutionizing Residential Spaces

The concept of smart homes and connected living epitomizes the integration of advanced technologies to enhance the comfort, convenience, and overall lifestyle of residents within smart cities. This paradigm shift transforms traditional residences into intelligent and responsive living spaces, leveraging a network of interconnected devices and systems.
One fundamental aspect of smart homes is the deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) devices that seamlessly communicate with each other. These devices include smart thermostats, lighting systems, security cameras, and appliances, all interconnected to form an intelligent ecosystem. For instance, smart thermostats learn user preferences over time, adjusting the temperature based on patterns of occupancy to optimize energy consumption. Companies like Google Nest and Amazon Ring exemplify the market’s growth in providing integrated smart home solutions.
Connected living extends beyond individual homes to entire residential areas. In smart neighborhoods, shared infrastructure and services are integrated, fostering a cohesive and technologically enhanced community experience. For example, Songdo International Business District in South Korea incorporates smart technologies into its urban planning, ensuring that residences, businesses, and public spaces are interconnected for improved efficiency and quality of life.
The rise of voice-activated virtual assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant, further contributes to the intelligence of smart homes. Residents can control various aspects of their living space, from adjusting lighting and temperature to managing home security, simply by issuing voice commands. This hands-free convenience enhances accessibility for individuals and underscores the user-friendly nature of smart home technologies.
Security and privacy are paramount concerns in the realm of smart homes. Advanced security systems, including biometric authentication, encrypted communication, and secure device management, help mitigate potential risks associated with interconnected devices. Residents can monitor and control their home security remotely through dedicated mobile apps, ensuring peace of mind even when away from home.
In conclusion, the integration of smart homes and connected living within smart cities is a transformative leap towards creating intelligent, efficient, and secure residential spaces. By seamlessly intertwining IoT devices, smart neighborhoods, and voice-activated interfaces, smart cities aim to elevate the quality of life for residents, fostering a more connected and technologically advanced urban living experience.
7. Digital Health in Urban Environments: Wellness Tech for City Dwellers
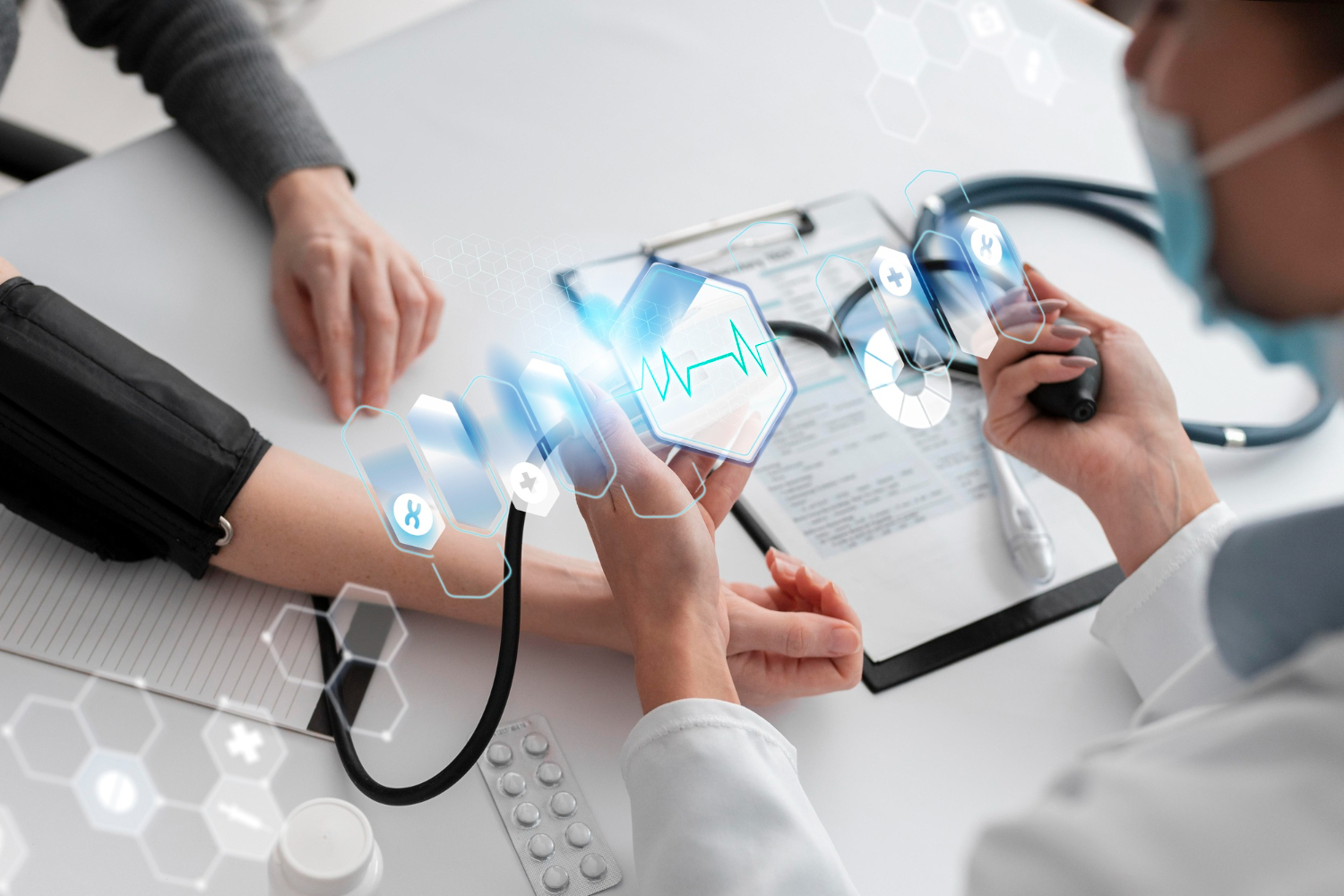

The convergence of digital health technologies within urban environments represents a groundbreaking approach to healthcare, leveraging innovative solutions to enhance wellness, improve accessibility, and streamline healthcare delivery for city dwellers. This intersection of technology and healthcare, often referred to as digital health, is revolutionizing how residents access and manage their health within the bustling landscape of smart cities.
One prominent aspect of digital health in urban environments is the adoption of wearable devices and health-tracking technologies. Devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers enable individuals to monitor various health metrics, including heart rate, physical activity, and sleep patterns. This data not only empowers individuals to take proactive measures for their well-being but also contributes to the creation of comprehensive health profiles that can aid healthcare providers in delivering personalized care. Cities like Singapore have embraced wearable technology as part of their Smart Nation initiative to promote healthier living.
Telemedicine, another key component of digital health, facilitates remote healthcare consultations and monitoring. Through video calls, mobile apps, and remote monitoring devices, city dwellers can access healthcare services without the need for physical visits to medical facilities. This is particularly valuable in urban areas where accessibility to healthcare providers may be constrained by distance or traffic congestion. The city of Barcelona, for example, has integrated telemedicine services to enhance healthcare accessibility for its residents.
Furthermore, smart city initiatives are incorporating health data analytics to gather insights into public health trends and risks. By aggregating anonymized health data from various sources, cities can identify patterns, predict potential health issues, and allocate resources more efficiently. This data-driven approach contributes to proactive public health management. London’s “Healthy Streets” initiative utilizes data analytics to assess the impact of urban design on public health, aiming to create healthier and more walkable urban spaces.
The integration of health-related apps and platforms into the smart city ecosystem further amplifies the impact of digital health. Mobile applications that provide real-time information on air quality, healthy food options, and fitness activities empower city residents to make informed choices that positively impact their well-being. In San Francisco, for instance, the “StreetAir” app allows users to check air quality in different neighborhoods, promoting awareness of environmental factors affecting health.
In conclusion, the incorporation of digital health in urban environments is a transformative step towards promoting wellness and improving healthcare accessibility for city dwellers. From wearable devices and telemedicine to data analytics and health-focused apps, smart cities are leveraging technology to create a more connected and health-conscious urban living experience.
8. Augmented Reality in Urban Planning: Visualizing Tomorrow’s Cities
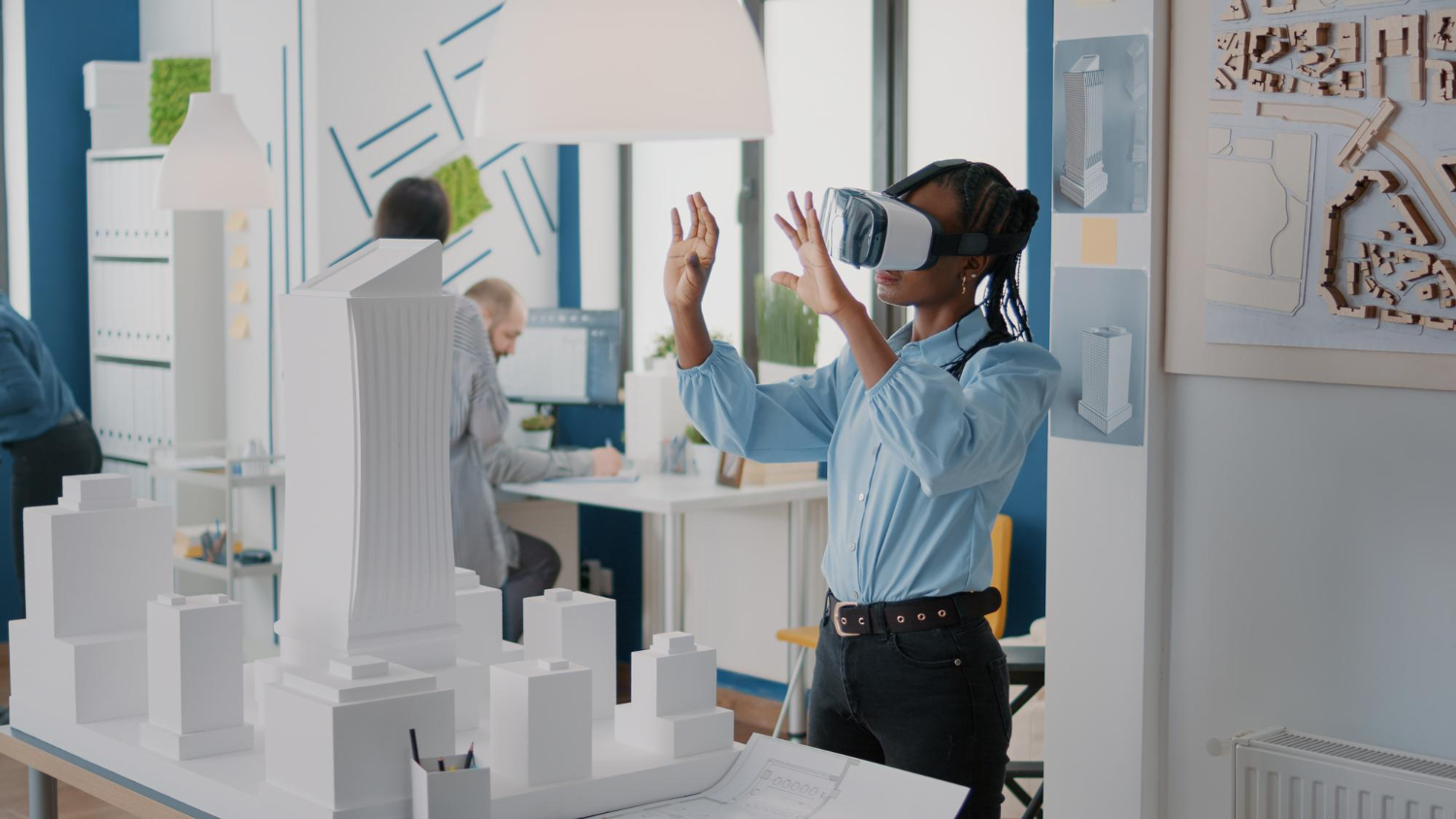

The infusion of augmented reality (AR) into urban planning signifies a transformative approach to envisioning and designing the cities of the future. Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical world, offering city planners, architects, and residents immersive tools to visualize and interact with urban spaces in unprecedented ways.
One key application of augmented reality in urban planning is the creation of interactive 3D models of proposed architectural developments. City planners and architects can use AR to superimpose virtual structures onto existing landscapes, allowing them to assess the visual impact and integration of new buildings seamlessly. This not only enhances the accuracy of design assessments but also facilitates community engagement by providing residents with a realistic preview of planned changes. For instance, the AR app used in the planning of London’s Nine Elms district allowed stakeholders to explore virtual representations of the upcoming development.
Furthermore, AR is utilized in creating “smart cities” that enhance the urban experience. For example, AR wayfinding systems can provide real-time navigation information, directing pedestrians to points of interest, public transportation hubs, and other essential locations. This not only improves mobility within the city but also fosters a more connected and informed urban environment. Cities like Helsinki have experimented with AR navigation apps to enhance the pedestrian experience.
Augmented reality also plays a role in historical preservation and cultural heritage. By overlaying digital reconstructions of historical sites onto the existing landscape, AR allows residents and visitors to virtually explore the past. This immersive experience contributes to a deeper understanding of a city’s history and cultural significance. Cities like Rome have incorporated AR to showcase historical layers and artifacts, enriching the cultural experience for residents and tourists alike.
Moreover, AR contributes to public participation in urban planning processes. Augmented reality applications can enable citizens to visualize proposed changes to their neighborhoods, fostering a sense of involvement in decision-making. This inclusivity enhances transparency in the planning process and allows for valuable community input. In Sydney, for instance, AR has been used to visualize proposed developments, encouraging public engagement and feedback.
In summary, augmented reality in urban planning offers a dynamic and interactive toolset for envisioning and shaping tomorrow’s cities. From designing architectural developments to improving navigation and preserving cultural heritage, AR empowers city planners and residents alike to actively participate in creating more vibrant, sustainable, and user-friendly urban environments.
9. Cybersecurity in Smart Cities: Safeguarding the Digital Urban Landscape

As smart cities embrace advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and connectivity, the imperative of robust cybersecurity measures becomes paramount. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, interconnected systems, and digitized services in urban landscapes necessitates a proactive and comprehensive approach to safeguarding against potential cyber threats.
One critical aspect of cybersecurity in smart cities is the protection of IoT devices. As these devices collect and transmit data in real-time, they become potential targets for cyberattacks. Security measures such as encryption, secure authentication, and regular software updates are crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect the integrity of the data. For instance, cities like Barcelona have implemented stringent security protocols for their IoT deployments, ensuring the resilience of smart city systems.
Interconnected systems within smart cities, ranging from traffic management to public services, require robust cybersecurity frameworks to prevent disruptions and unauthorized access. Implementing network segmentation, encryption, and intrusion detection systems are vital strategies to safeguard the integrity and functionality of these critical systems. In Singapore, for example, the government has implemented a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that includes regular audits and exercises to assess and enhance the resilience of its smart city infrastructure.
Moreover, the protection of citizen data is a fundamental aspect of cybersecurity in smart cities. With the proliferation of digital services, including smart healthcare, e-governance, and data-driven urban planning, ensuring the confidentiality and privacy of personal information is paramount. Cities are adopting stringent data protection measures, including encryption, anonymization, and secure storage, to mitigate the risks associated with potential data breaches. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) serves as a regulatory framework influencing data protection practices in smart cities like Amsterdam.
Cybersecurity awareness and education initiatives play a crucial role in building a resilient digital urban landscape. Training city officials, employees, and citizens on best practices for online security and fostering a cybersecurity-conscious culture contribute to a collective effort in mitigating cyber threats. In the United States, cities such as New York have implemented cybersecurity awareness programs to educate both government personnel and the public.
In summary, cybersecurity in smart cities is an integral component to ensure the reliability, privacy, and functionality of digital urban landscapes. From securing IoT devices and interconnected systems to protecting citizen data and fostering cybersecurity awareness, cities are actively working towards creating resilient and secure environments for their inhabitants. The dynamic nature of cyber threats necessitates an ongoing commitment to staying ahead of potential risks and ensuring the longevity of smart city initiatives.
10. Blockchain Applications: Ensuring Transparency and Trust in City Operations

The integration of blockchain technology in smart cities marks a paradigm shift towards enhancing transparency, accountability, and trust in various aspects of city operations. Blockchain, a decentralized and distributed ledger technology, provides a secure and tamper-resistant framework for recording transactions and data. This innovation holds the potential to transform how cities manage processes, ensuring a higher level of integrity and reliability.
One primary application of blockchain in smart cities is in the realm of transparent and secure governance. By utilizing blockchain for recording and verifying public records, such as property transactions, permits, and licenses, cities can create an immutable and auditable trail of information. This ensures transparency, reduces the risk of fraud, and enhances the efficiency of administrative processes. Dubai, for example, has launched the “Blockchain Strategy,” aiming to shift all government transactions to the blockchain by 2020 to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of disputes.
Another significant application is in the domain of supply chain management. Blockchain enables end-to-end visibility and traceability of goods as they move through the supply chain. This is particularly valuable in urban environments where efficient and transparent supply chains are essential. Cities can use blockchain to track the sourcing, transportation, and delivery of goods, enhancing accountability and reducing the likelihood of counterfeit products entering the market.
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, represent a powerful application of blockchain in city operations. These contracts automate and enforce predefined rules without the need for intermediaries, reducing bureaucracy and ensuring trust in transactions. For instance, a smart contract could automate and streamline the processes involved in public services, ensuring a more efficient and reliable delivery of services to residents.
Furthermore, blockchain enhances the security and integrity of data in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. As IoT devices generate and exchange vast amounts of data, using blockchain to secure this data ensures that it remains unaltered and trustworthy. This is crucial in applications such as smart grids, where data accuracy is paramount for efficient energy distribution. Amsterdam’s “City Sensor” project explores the use of blockchain to secure and manage data from various IoT devices deployed across the city.
In conclusion, blockchain applications in smart cities are instrumental in fostering transparency, trust, and efficiency across various sectors. From governance and supply chain management to the implementation of smart contracts and securing IoT data, blockchain technology contributes to building a resilient and reliable foundation for the cities of the future. As cities continue to explore innovative solutions, blockchain stands out as a key enabler of transparent and trustworthy urban operations.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for the Smart Urban Future
The journey towards smart cities is not just a technological evolution but a holistic transformation that reshapes how we live, work, and interact within urban environments. In this exploration of “Smart Cities, Smart Startups: Tech Innovations for Urban Living,” we’ve delved into a spectrum of groundbreaking technologies poised to redefine the urban landscape.
From the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) forming the nervous system of smart cities to the revolutionizing concept of sustainable urban mobility, where innovative energy solutions power the urban future, each facet contributes to a vision of cities that are intelligent, efficient, and sustainable. The infusion of artificial intelligence into infrastructure, the adoption of data-driven governance, and the rise of augmented reality in urban planning showcase the technological prowess transforming the very foundations of city management and design.
Smart homes and connected living bring technology closer to residents, promising enhanced comfort and convenience, while digital health initiatives underscore a commitment to the well-being of city dwellers. As cities embrace blockchain for transparency and trust, and prioritize robust cybersecurity measures, they fortify the digital foundations essential for the smart urban future.
In this era of unprecedented innovation, smart cities are not just about technological marvels but about creating a seamless, interconnected, and inclusive urban experience. The collaborative efforts of city planners, tech innovators, and residents pave the way for a future where cities not only leverage technology for efficiency but also prioritize sustainability, resilience, and the well-being of their inhabitants.
The journey towards smart cities is dynamic, with each innovation contributing a brushstroke to the canvas of urban evolution. As we look ahead, the promise of smart cities lies not just in the technological advancements showcased here but in the potential for these innovations to forge a path towards a more livable, sustainable, and interconnected urban future. The journey has just begun, and the possibilities are boundless as we navigate the landscape of tomorrow’s smart cities.
Also Read :Does The Junk-Bond Market’s Resilience Suggest a Soft Landing For The US Economy? 2024
Read More on Google Click here









0 Comments